Lesson 3
Introduction
In this lesson there are few things to be understood and few to learn. Go through this lesson again and again. Things which are not clear to you leave them. You will learn them as you go to the next lessons and things will be more clear.
Understand
- Understand and use the abbreviations.
- All abbreviations must be learnt
- Understand fully the terminology used
- Understand fully the term agnate, cognate
Learn & remember
- Learn Order of Heirs
- Learn names of heirs
Very important to know
- All Relations mentioned in inheritance are to the person died
- Person died can be male or female
- Father means father of the person died, son means son of the person died
- If a heir is not alive then he does not inherit.
E.g. A has died leaving 2 sons and 2 daughters. But A had one more son who had died before A’s death. Here the dead son does not inherit.
Abbreviations
| H | Husband |
| W | Wife |
| D | Daughter |
| S | Son |
| SS | Son’s son |
| SD | Son’s daughter |
| SSD | Son’s son’s daughter |
| F | Father |
| M | Mother |
| TGF | True grand father |
| TGM | True grand mother |
| FM | Father’s mother |
| MM | Mother’s mother |
| Bf | Brother full |
| Bc | Brother consanguineous |
| Bu | Brother uterine |
| Sf | Sister full |
| Sc | Sister consanguineous |
| Su | Sister uterine |
| PUf | Paternal uncle full |
| PUc | Paternal uncle consanguineous |
| PUu | Paternal uncle uterine |
| PUfS | Son of Puf |
| PUcS | Son of PUc |
| PA | Paternal aunt |
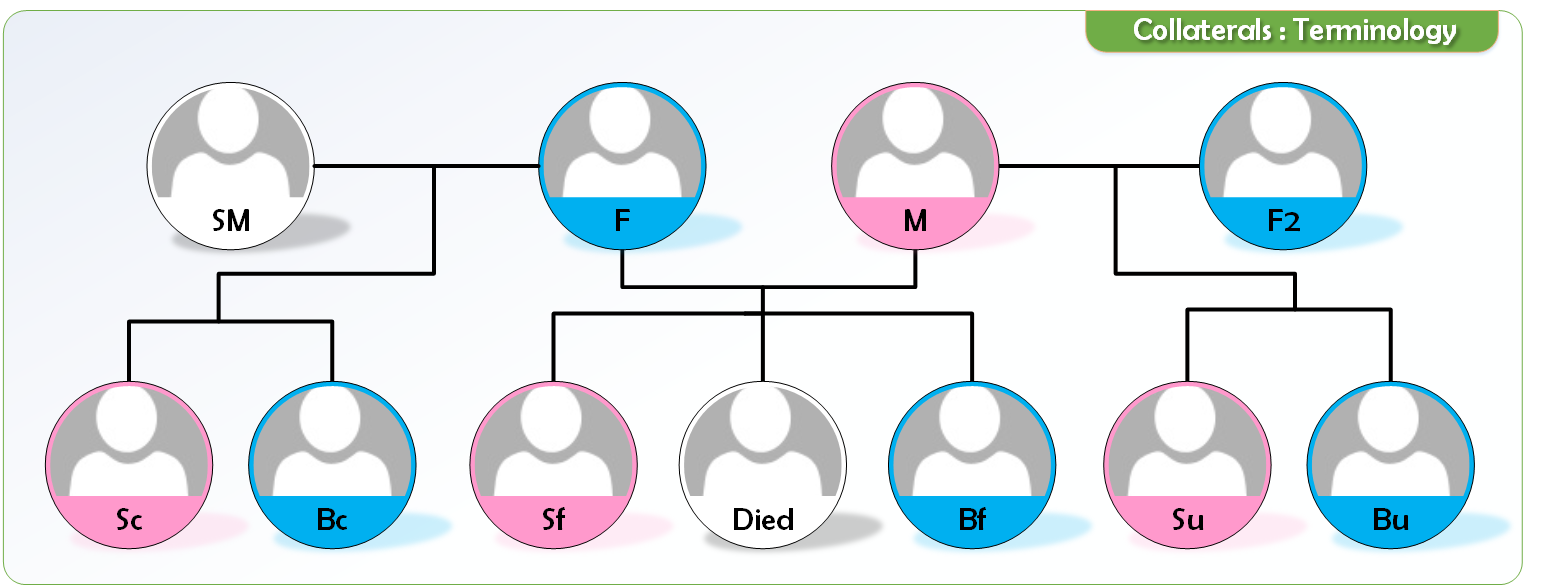
Terminology: Full & consanguineous
| Full brother /sister | Brothers from same father same mother |
| Consanguineous brother/sister Paternal half brother/sister |
Same father different mother |
| Uterine brother/sister maternal half brother/sister |
Same mother different father. This can arise in 2 situations. 1. Mother has married the father after the death of first husband. 2. Father has died and mother has married again. |
Terminology: Agnate
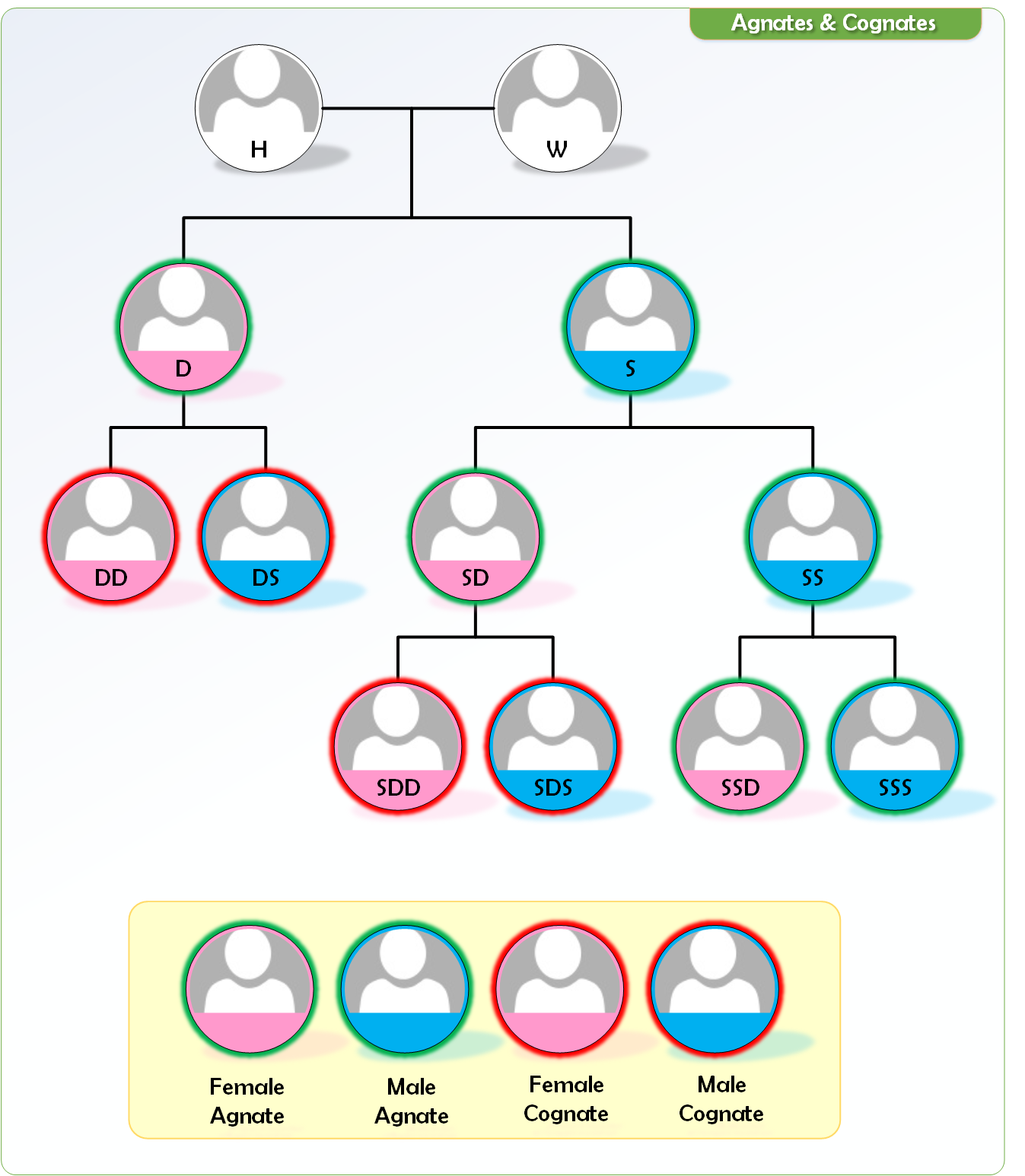
Agnate = a person is called agnate when he /she can be traced to the deceased (or the person whose inheritors are to be decided ) without a female link. Person died can be male or female and the heir can be male or female but the link in between must be males only.
Only the link should be males.
- Agnatic Ascendants
- male - F, FF, FFF
- female - FM, FFM
- Agnatic descendants
- male S,SS, SSS
- female D, SD, SSD
- Agnatic Collaterals
- male - Bf, Bc, BfS,BcS, PUf, PUc, PUS
- female Sf, Sc, BfD…
- Cognate = female link between the person and the deceased
e.g.: DD, Mother’s father, sisters son
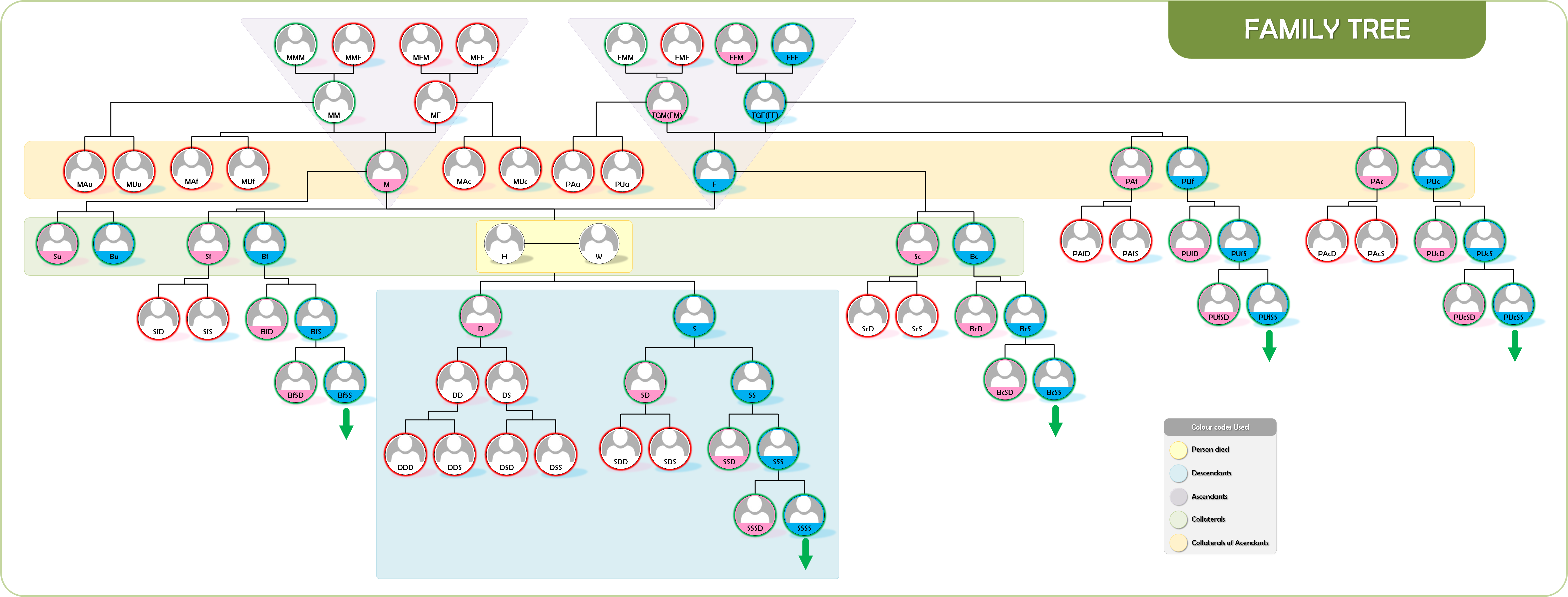
Understanding of this in a family tree is required for the following reasons
- It decides the persons for residual shares - Asaba or balance heirs. All male agnates are in this category
- It is required in calculation of shares of H,W,F,M,TGF
In the family tree below blue colour with green border indicates male agnates and pink colour with green border indicates female agnates
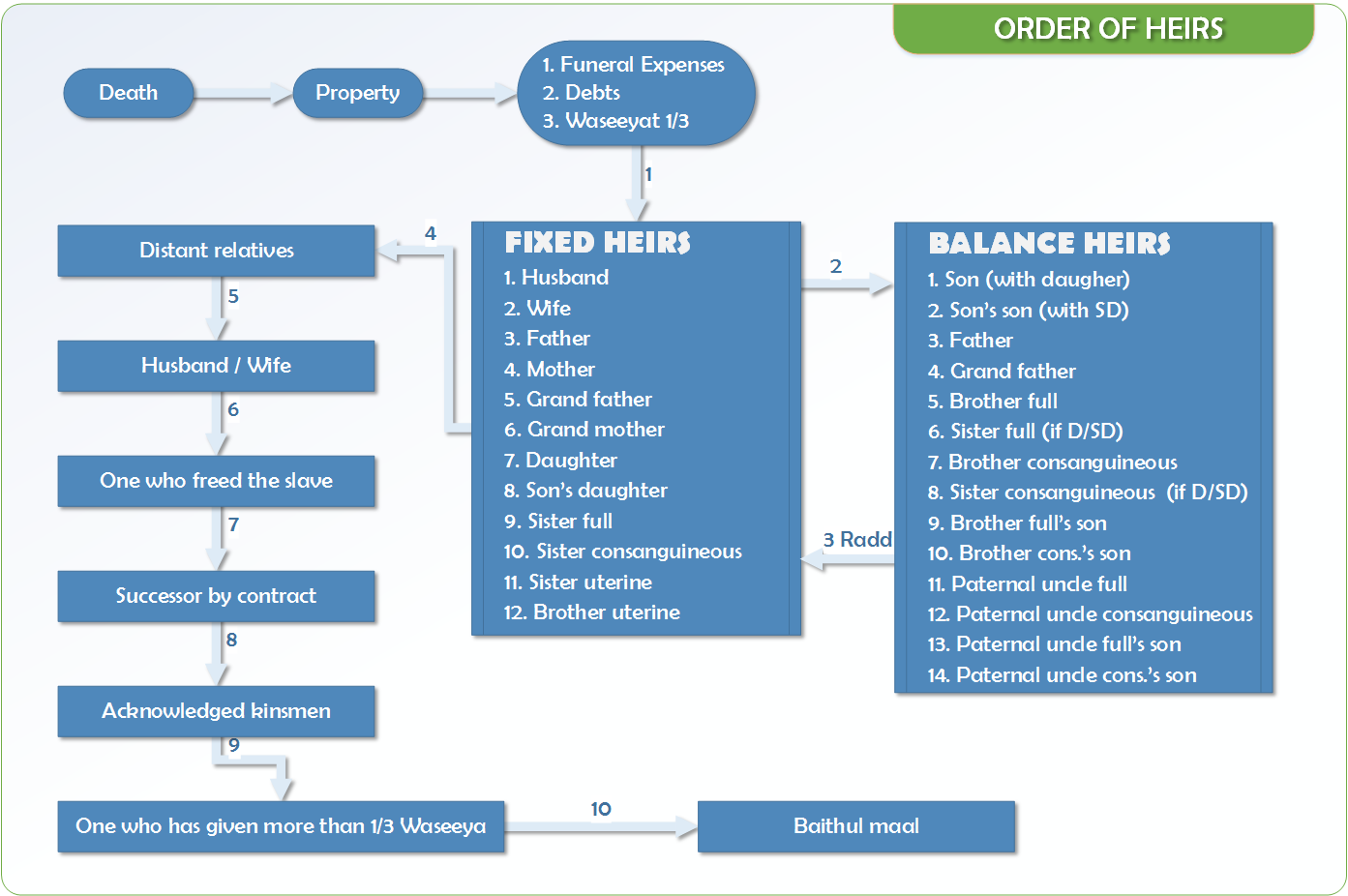
Heirs
- Fixed share Heirs - 12 in number
- Balance share heirs - male agnates
- Radd – fixed heirs as balance heirs if group 2 are not there
- Distant blood relatives- in the absence of above 1&2 – All blood relatives excluding 1&2 groups are included here
- Spouse in the absence of above
- One who freed the slave
- Successor by contract
- Acknowledged kinsmen
- One who was given more than 1/3 as waseeyat
- Baithul maal
Classification of Heirs
Based on importance:
- Primary Heirs :Always inherit – e.g. H, W, F, M, S, D (Never excluded)
- Secondary Heirs: Excluded by other heirs e.g. Bf, SS
Based on nature of relationship:
- Relations by blood
- Relations by affinity-marriage
Let us discuss these classes in detail.
Principle Classes — of prime importance
- Fixed share Heirs
- Residuary Share Heirs
- Distant Kindred
Secondary Classes — of less importance
- Freeing of a slave
- If a slave who has been freed dies and there are no residuary to take the balance then the master who freed the slave becomes a residuary. Some place this class above the distant kindred. In the present day this is of no significance
- Successor by contract
- A successor by contract is a person with whom the deceased has made a contract to inherit his property after his death for some consideration. Shafei, Maliki and Hanbali do not recognize
- Acknowledged kinsmen
- Here the deceased has acknowledges some one else from a different family as his kinship. E.g.. Person recognizes someone as his brother (kinship through father) or as uncle (kinship through grandfather). Acknowledgement of kinship through oneself like accepting someone as son is not considered as acknowledged kinsmen. Shafei do not recognise this
- One who was given >1/3 as waseeyat
- In the absence of above all if there are no one then the person who has been mentioned in the waseeyat or the will takes the inheritance
Order of priority: Heirs
- Quranic sharers - Fixed share Heirs - 12 in number
- Asaba or residuary heirs or Balance share heirs - male agnates
- Sharers to excess - Radd – fixed heirs as balance heirs if group 2 are not there(except spouses)
- Distant blood relatives
- Spouse who become heirs to excess
- One who freed the slave
- Successor by contract
- Acknowledged kinsmen
- One who was given more than 1/3 as waseeyat
- Baithul maal
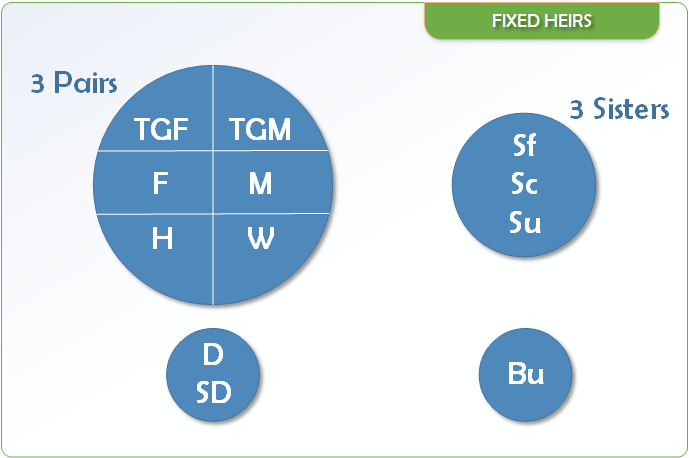
Fixed Share Heirs
They can be classified in to three groups:
- Only fixed shares : 6 –H, W, M, TGM, Bu, Su
- Either fixed or balance shares : 4 – D, SD, Sf, Sc
- Both fixed and/or balance share : 2 – F, TGF
Another classification can be made as per their relationship with the deceased:
- Heirs by Affinity:
1.Husband, 2.Wife - Ascendants:
3.Father, 4.Mother, 5.TGF, 6.TGM - Descendants:
7.Daughter, 8.Son’s daughter - Collaterals:
9.Sister full, 10.Sister consang., 11.Sister uterine, 12.Brother uterine.
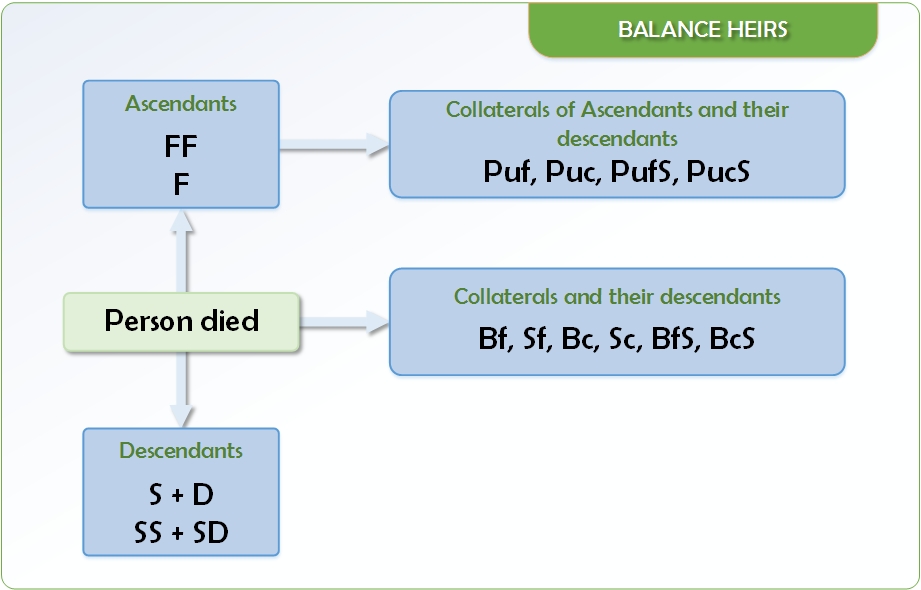
Balance Heirs (Asaba)
| Male | 1. Son |
|---|---|
| 2. Son’s son… | |
| 3. Father | |
| 4. True grand father | |
| 5. Brother full | |
| 6. Brother consanguineous | |
| 7. Brother full’s son | |
| 8. Brother consang.’s son | |
| 9. Paternal uncle full | |
| 10. Paternal uncle consang. | |
| 11. Paternal uncle full's son | |
| 12. Paternal uncle consang's son | |
| 13. Releaser of a slave | |
| Female | 1. Daughter |
| 2. Son's Daughter | |
| 3. Sister full | |
| 4. Sister consanguineous | |
| 5. Releaser of a slave |
Each Sharer - Characteristics
In the coming chapters the following charecteristics of each sharer will be described in detail:
- Primary or Secondary
- Excluded by e.g.; FM excluded by F
- Excludes e.g.: S excludes all B & S
- Share fraction and the conditions favouring them
- Effect on other sharer e.g.; S and D reduce spouse’ share
- Effect of other sharers on the person e.g.; M share reduced by 2 or more B/S
- Special occasions
